Wolfgang Hoppe, Jonathan Weber, Saban Tirpanci, Oliver Gueckstock, Tobias Kampfrath, Georg Woltersdorf,
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsanm.1c01449
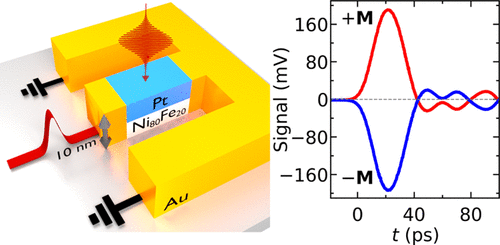
We generate ultrafast current pulses by optical means with the aid of the inverse spin Hall effect. In ferromagnet/normal metal bilayer structures, intense spin current pulses are generated by optical pumping with intense femtosecond laser pulses. Subsequently, the spin current pulses are converted into a charge current pulse via the inverse spin Hall effect and launched into waveguide structures. The electrical signals are detected using a sampling oscilloscope. We propose to use these nanolayered emitters to act as on-chip THz sources and robust ultrafast photodetectors, which can be combined with metallic waveguide structures. In doing so, the on-chip control of THz fields becomes possible on the nanometer scale.

No comments:
Post a Comment