Qin Wang, Xinliang Wang, Liwei Zhang, Yongqiang Wang, Wentao Qiao, Xu Han, Xiaolin Cai, and Weiyang Yu
https://www.osapublishing.org/ao/abstract.cfm?uri=ao-58-1-94&origin=search
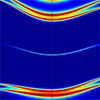
The transmission properties of one-dimensional photonic crystals (PCs) containing a metamaterial (MM) defect layer are investigated using the transfer matrix method. The MM is composed of alternating layers of a dielectric material and a Dirac semimetal (DS) material. Numerical results show that the defective PCs possess a tunable defect mode, which is significantly dependent on the Fermi level of the DS as well as the structural parameters of the MM defect layer. The defect mode properties under different incident angles for TE and TM polarizations are also studied. Such defective structures have potential applications in tunable filters and sensors in terahertz regions.
© 2018 Optical Society of America